This example uses a custom item model,
FileSystemModel
,和
QCompleter
对象。
QCompleter
is a class that provides completions based on an item model. The type of model, the completion mode, and the case sensitivity can be selected using combo boxes.
The Completer example requires a resource file in order to store the countries.txt and words.txt . The resource file contains the following code:
<!DOCTYPE RCC><RCC version="1.0"> <qresource prefix="/"> <file>resources/countries.txt</file> <file>resources/wordlist.txt</file> </qresource> </RCC>
The
FileSystemModel
类是子类化的
QFileSystemModel
, which provides a data model for the local filesystem.
class FileSystemModel : public QFileSystemModel { public: FileSystemModel(QObject *parent = 0); QVariant data(const QModelIndex &index, int role = Qt::DisplayRole) const override; };
This class only has a constructor and a
data()
function as it is only created to enable
data()
to return the entire file path for the display role, unlike
QFileSystemModel
's
data()
function that only returns the folder and not the drive label. This is further explained in
FileSystemModel
's implementation.
The constructor for the
FileSystemModel
class is used to pass
parent
to
QFileSystemModel
.
FileSystemModel::FileSystemModel(QObject *parent) : QFileSystemModel(parent) { }
As mentioned earlier, the
data()
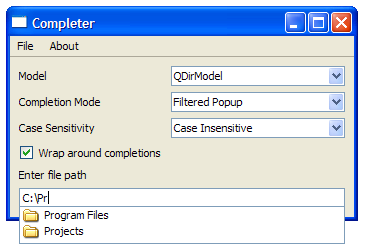
function is reimplemented in order to get it to return the entire file parth for the display role. For example, with a
QFileSystemModel
, you will see "Program Files" in the view. However, with
FileSystemModel
, you will see "C:\Program Files".
QVariant FileSystemModel::data(const QModelIndex &index, int role) const { if (role == Qt::DisplayRole && index.column() == 0) { QString path = QDir::toNativeSeparators(filePath(index)); if (path.endsWith(QDir::separator())) path.chop(1); return path; } return QFileSystemModel::data(index, role); }
The screenshots below illustrate this difference:

|
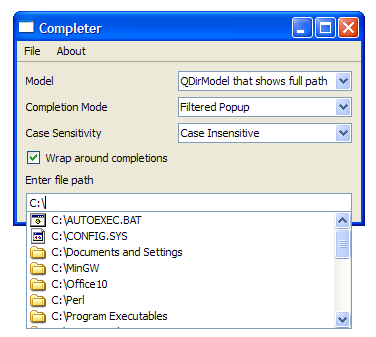
|
The Qt::EditRole , which QCompleter uses to look for matches, is left unchanged.
The
MainWindow
类是子类化的
QMainWindow
and implements five private slots -
about()
,
changeCase()
,
changeMode()
,
changeModel()
,和
changeMaxVisible()
.
class MainWindow : public QMainWindow { Q_OBJECT public: MainWindow(QWidget *parent = 0); private slots: void about(); void changeCase(int); void changeMode(int); void changeModel(); void changeMaxVisible(int);
在
MainWindow
class, we have two private functions:
createMenu()
and
modelFromFile()
. We also declare the private widgets needed - three
QComboBox
objects, a
QCheckBox
,
QCompleter
,
QLabel
,和
QLineEdit
.
private: void createMenu(); QAbstractItemModel *modelFromFile(const QString& fileName); QComboBox *caseCombo; QComboBox *modeCombo; QComboBox *modelCombo; QSpinBox *maxVisibleSpinBox; QCheckBox *wrapCheckBox; QCompleter *completer; QLabel *contentsLabel; QLineEdit *lineEdit; };
The constructor of
MainWindow
constructs a
MainWindow
with a parent widget and initializes the private members. The
createMenu()
function is then invoked.
We set up three
QComboBox
对象,
modelComb
,
modeCombo
and
caseCombo
. By default, the
modelCombo
被设为
QFileSystemModel
,
modeCombo
is set to "Filtered Popup" and the
caseCombo
is set to "Case Insensitive".
MainWindow::MainWindow(QWidget *parent) : QMainWindow(parent), completer(0), lineEdit(0) { createMenu(); QWidget *centralWidget = new QWidget; QLabel *modelLabel = new QLabel; modelLabel->setText(tr("Model")); modelCombo = new QComboBox; modelCombo->addItem(tr("QFileSytemModel")); modelCombo->addItem(tr("QFileSytemModel that shows full path")); modelCombo->addItem(tr("Country list")); modelCombo->addItem(tr("Word list")); modelCombo->setCurrentIndex(0); QLabel *modeLabel = new QLabel; modeLabel->setText(tr("Completion Mode")); modeCombo = new QComboBox; modeCombo->addItem(tr("Inline")); modeCombo->addItem(tr("Filtered Popup")); modeCombo->addItem(tr("Unfiltered Popup")); modeCombo->setCurrentIndex(1); QLabel *caseLabel = new QLabel; caseLabel->setText(tr("Case Sensitivity")); caseCombo = new QComboBox; caseCombo->addItem(tr("Case Insensitive")); caseCombo->addItem(tr("Case Sensitive")); caseCombo->setCurrentIndex(0);
The
maxVisibleSpinBox
is created and determines the number of visible item in the completer
The
wrapCheckBox
is then set up. This
checkBox
determines if the
completer
's
setWrapAround()
property is enabled or disabled.
QLabel *maxVisibleLabel = new QLabel;
maxVisibleLabel->setText(tr("Max Visible Items"));
maxVisibleSpinBox = new QSpinBox;
maxVisibleSpinBox->setRange(3,25);
maxVisibleSpinBox->setValue(10);
wrapCheckBox = new QCheckBox;
wrapCheckBox->setText(tr("Wrap around completions"));
wrapCheckBox->setChecked(true);
We instantiate
contentsLabel
and set its size policy to
fixed
. The combo boxes'
activated()
signals are then connected to their respective slots.
contentsLabel = new QLabel;
contentsLabel->setSizePolicy(QSizePolicy::Fixed, QSizePolicy::Fixed);
connect(modelCombo, SIGNAL(activated(int)), this, SLOT(changeModel()));
connect(modeCombo, SIGNAL(activated(int)), this, SLOT(changeMode(int)));
connect(caseCombo, SIGNAL(activated(int)), this, SLOT(changeCase(int)));
connect(maxVisibleSpinBox, SIGNAL(valueChanged(int)), this, SLOT(changeMaxVisible(int)));
The
lineEdit
is set up and then we arrange all the widgets using a
QGridLayout
。
changeModel()
function is called, to initialize the
completer
.
lineEdit = new QLineEdit;
QGridLayout *layout = new QGridLayout;
layout->addWidget(modelLabel, 0, 0); layout->addWidget(modelCombo, 0, 1);
layout->addWidget(modeLabel, 1, 0); layout->addWidget(modeCombo, 1, 1);
layout->addWidget(caseLabel, 2, 0); layout->addWidget(caseCombo, 2, 1);
layout->addWidget(maxVisibleLabel, 3, 0); layout->addWidget(maxVisibleSpinBox, 3, 1);
layout->addWidget(wrapCheckBox, 4, 0);
layout->addWidget(contentsLabel, 5, 0, 1, 2);
layout->addWidget(lineEdit, 6, 0, 1, 2);
centralWidget->setLayout(layout);
setCentralWidget(centralWidget);
changeModel();
setWindowTitle(tr("Completer"));
lineEdit->setFocus();
}
The
createMenu()
function is used to instantiate the
QAction
objects needed to fill the
fileMenu
and
helpMenu
. The actions'
triggered()
signals are connected to their respective slots.
void MainWindow::createMenu() { QAction *exitAction = new QAction(tr("Exit"), this); QAction *aboutAct = new QAction(tr("About"), this); QAction *aboutQtAct = new QAction(tr("About Qt"), this); connect(exitAction, SIGNAL(triggered()), qApp, SLOT(quit())); connect(aboutAct, SIGNAL(triggered()), this, SLOT(about())); connect(aboutQtAct, SIGNAL(triggered()), qApp, SLOT(aboutQt())); QMenu* fileMenu = menuBar()->addMenu(tr("File")); fileMenu->addAction(exitAction); QMenu* helpMenu = menuBar()->addMenu(tr("About")); helpMenu->addAction(aboutAct); helpMenu->addAction(aboutQtAct); }
The
modelFromFile()
function accepts the
fileName
of a file and processes it depending on its contents.
We first validate the
file
to ensure that it can be opened in
QFile::ReadOnly
mode. If this is unsuccessful, the function returns an empty
QStringListModel
.
QAbstractItemModel *MainWindow::modelFromFile(const QString& fileName) { QFile file(fileName); if (!file.open(QFile::ReadOnly)) return new QStringListModel(completer);
The mouse cursor is then overridden with
Qt::WaitCursor
before we fill a
QStringList
对象,
words
, with the contents of
file
. Once this is done, we restore the mouse cursor.
#ifndef QT_NO_CURSOR QApplication::setOverrideCursor(QCursor(Qt::WaitCursor)); #endif QStringList words; while (!file.atEnd()) { QByteArray line = file.readLine(); if (!line.isEmpty()) words << line.trimmed(); } #ifndef QT_NO_CURSOR QApplication::restoreOverrideCursor(); #endif
As mentioned earlier, the resources file contains two files -
countries.txt
and
words.txt
。若
file
read is
words.txt
, we return a
QStringListModel
with
words
as its
QStringList
and
completer
as its parent.
if (!fileName.contains(QLatin1String("countries.txt")))
return new QStringListModel(words, completer);
若
file
read is
countries.txt
, then we require a
QStandardItemModel
with
words.count()
rows, 2 columns, and
completer
as its parent.
QStandardItemModel *m = new QStandardItemModel(words.count(), 2, completer);
A standard line in countries.txt is:
Norway NO
Hence, to populate the
QStandardItemModel
对象,
m
, we have to split the country name and its symbol. Once this is done, we return
m
.
for (int i = 0; i < words.count(); ++i) {
QModelIndex countryIdx = m->index(i, 0);
QModelIndex symbolIdx = m->index(i, 1);
QString country = words[i].mid(0, words[i].length() - 2).trimmed();
QString symbol = words[i].right(2);
m->setData(countryIdx, country);
m->setData(symbolIdx, symbol);
}
return m;
}
The
changeMode()
function sets the
completer
's mode, depending on the value of
index
.
void MainWindow::changeMode(int index) { QCompleter::CompletionMode mode; if (index == 0) mode = QCompleter::InlineCompletion; else if (index == 1) mode = QCompleter::PopupCompletion; else mode = QCompleter::UnfilteredPopupCompletion; completer->setCompletionMode(mode); }
The
changeModel()
function changes the item model used based on the model selected by the user.
A
switch
statement is used to change the item model based on the index of
modelCombo
。若
case
is 0, we use an unsorted
QFileSystemModel
, providing us with a file path excluding the drive label.
void MainWindow::changeModel() { delete completer; completer = new QCompleter(this); completer->setMaxVisibleItems(maxVisibleSpinBox->value()); switch (modelCombo->currentIndex()) { default: case 0: { // Unsorted QFileSystemModel QFileSystemModel *fsModel = new QFileSystemModel(completer); fsModel->setRootPath(""); completer->setModel(fsModel); contentsLabel->setText(tr("Enter file path")); } break;
Note that we create the model with
completer
as the parent as this allows us to replace the model with a new model. The
completer
will ensure that the old one is deleted the moment a new model is assigned to it.
若
case
is 1, we use the
DirModel
we defined earlier, resulting in full paths for the files.
case 1:
{ // FileSystemModel that shows full paths
FileSystemModel *fsModel = new FileSystemModel(completer);
completer->setModel(fsModel);
fsModel->setRootPath("");
contentsLabel->setText(tr("Enter file path"));
}
break;
当
case
is 2, we attempt to complete names of countries. This requires a
QTreeView
对象,
treeView
. The country names are extracted from
countries.txt
and set the popup used to display completions to
treeView
.
case 2:
{ // Country List
completer->setModel(modelFromFile(":/resources/countries.txt"));
QTreeView *treeView = new QTreeView;
completer->setPopup(treeView);
treeView->setRootIsDecorated(false);
treeView->header()->hide();
treeView->header()->setStretchLastSection(false);
treeView->header()->setSectionResizeMode(0, QHeaderView::Stretch);
treeView->header()->setSectionResizeMode(1, QHeaderView::ResizeToContents);
contentsLabel->setText(tr("Enter name of your country"));
}
break;
The screenshot below shows the Completer with the country list model.
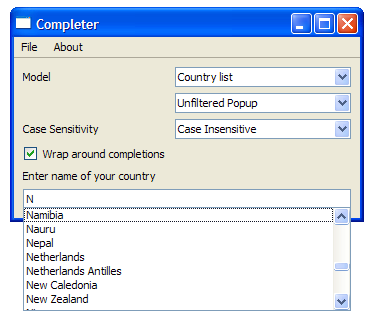
若
case
is 3, we attempt to complete words. This is done using a
QStringListModel
that contains data extracted from
words.txt
. The model is sorted
case insensitively
.
The screenshot below shows the Completer with the word list model.
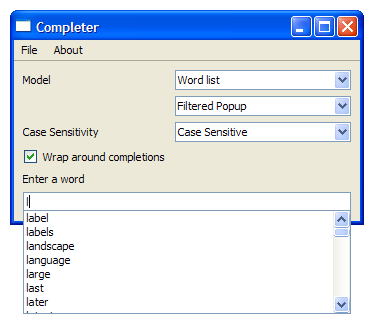
Once the model type is selected, we call the
changeMode()
函数和
changeCase()
function and set the wrap option accordingly. The
wrapCheckBox
's
clicked()
信号被连接到
completer
's
setWrapAround()
槽。
case 3:
{ // Word list
completer->setModel(modelFromFile(":/resources/wordlist.txt"));
completer->setModelSorting(QCompleter::CaseInsensitivelySortedModel);
contentsLabel->setText(tr("Enter a word"));
}
break;
}
changeMode(modeCombo->currentIndex());
changeCase(caseCombo->currentIndex());
completer->setWrapAround(wrapCheckBox->isChecked());
lineEdit->setCompleter(completer);
connect(wrapCheckBox, SIGNAL(clicked(bool)), completer, SLOT(setWrapAround(bool)));
}
The
changeMaxVisible()
update the maximum number of visible items in the completer.
void MainWindow::changeMaxVisible(int max) { completer->setMaxVisibleItems(max); }
The
about()
function provides a brief description about the example.
void MainWindow::about() { QMessageBox::about(this, tr("About"), tr("This example demonstrates the " "different features of the QCompleter class.")); }
main()
函数
The
main()
function instantiates
QApplication
and
MainWindow
and invokes the
show()
函数。
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { Q_INIT_RESOURCE(completer); QApplication app(argc, argv); MainWindow window; window.show(); return app.exec(); }
文件: